Holography
Basic Concepts
Holography is a technique that uses the interference and diffraction of light to record and display three-dimensional images. Hologram is a photographic technique that records the light scattered from an object, and uses that information to display a 3D image of the original object
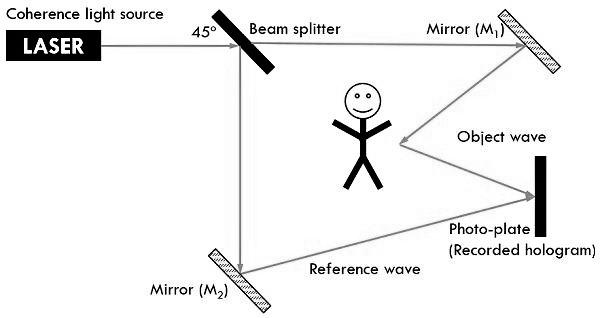
Recording of Hologram
The process of recording a hologram involves shining a laser beam onto an object, which reflects a portion of the beam onto a recording medium, such as holographic film or a holographic plate. A second beam, known as the reference beam, is directed onto the recording medium at a different angle. The interference between the two beams creates a pattern on the recording medium that is a record of the object's wavefront.
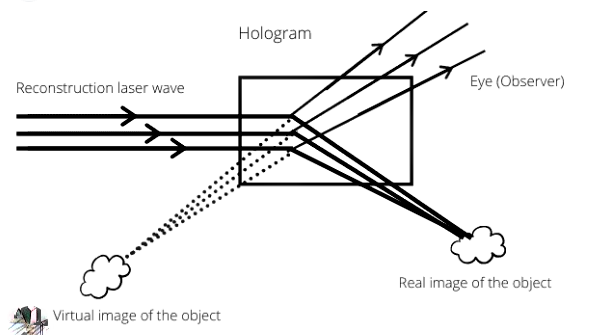
Reconstruction of Holograms
To reconstruct a hologram, a laser beam is directed onto the holographic plate. The light scattered by the hologram interferes with the reference beam to create a three-dimensional image of the original object.
Comparison with Photography
| Holography | Photography |
|---|---|
| Records three dimensional image of object | Records two dimensional image of object |
| Records the phase and amplitude of light waves | Records only the amplitude of light waves |
| Holograph is due to interference between object wave and reference wave | Photograph plate records the intensity variation of light reflected from object |
| If broken into pieces, the full information of object can be degenerated from each piece | If broken into pieces, each piece will provide only the partial information of the object |
| Requires laser light source for reconstruction | Does not require special light source for viewing |
| Can store multiple views in a single hologram | Stores only a single view per photograph |
Applications of Holography
Holography has a wide range of applications in various fields such as science, technology, medicine, and art. Some of the most notable applications are:
-
Optics and Laser Technology
- Laser beam steering and shaping
- Optical data storage and retrieval
- Optical communication and signal processing
- Interferometry and metrology
-
Security and Surveillance
- Security holograms on credit cards, passports, and other identification documents
- Holographic imaging for surveillance and identification
-
Art and Entertainment
- Holographic projections for live performances and events
- Holographic displays for virtual reality and augmented reality experiences
-
Medical and Biological Sciences
- Holographic microscopy and imaging
- Holographic laser tweezers for manipulation of biological samples